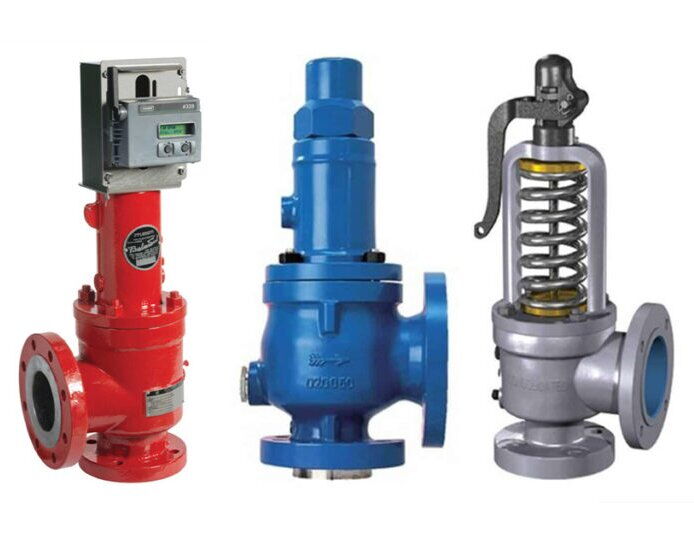
Comparing Roles of Control Valves and Safety Valves in Pipeline Systems
Control valves and safety valves are crucial components within pipeline systems, responsible respectively for regulating fluid flow and maintaining safe operating pressures, thereby safeguarding against overpressure hazards. Widely applied in industrial and construction sectors, these control valves and safety valves are essential not only for ensuring system functionality and production efficiency but also directly impacting equipment and personnel safety. Therefore, a thorough understanding and comparison of their functions, design principles, and operational characteristics are paramount for ensuring pipeline system stability and safety.
Function and Characteristics of Control Valves
Control valves are primarily used to precisely manage the flow rate, pressure, and temperature of fluid media within pipeline systems. Typically integrated with automated control systems, they adjust valve openings based on sensor feedback to maintain stable system operation under design conditions. Control valves play a critical role in industrial processes, such as chemical production, where they regulate fluid flow according to varying process requirements to ensure product quality and production efficiency. Designed for high-precision control performance and rapid response, they are suitable for diverse engineering environments and process flows.
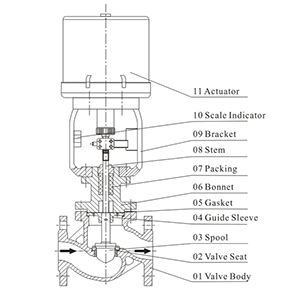
Functions and Applications of Safety Valves
Safety valves activate automatically to release pressure when internal pressures exceed preset safety thresholds, thereby protecting systems from damage due to overpressure. Commonly deployed in emergencies within boilers, pressure vessels, or other enclosed systems, safety valves prevent equipment damage or safety incidents caused by excessive pressure. The design and calibration of safety valves adhere strictly to standards and regulations to ensure reliable operation during critical moments.
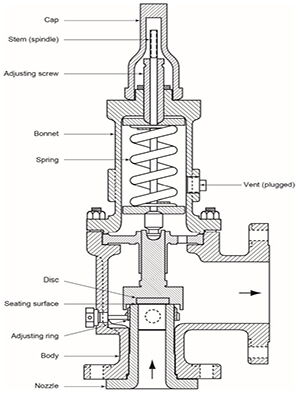
Comparison of Technical Design and Operating Principles
From a technical perspective, control valves and safety valves exhibit significant differences in design principles and operational modes. Control valves achieve precise control of fluid flow and pressure by adjusting valve positions or openings actively and flexibly in response to system requirements. In contrast, safety valves operate passively, triggering only when pressure reaches set limits to maintain system safety and stability.
Integrated Considerations and Practical Applications
In practical engineering applications, the judicious selection and configuration of control valves and safety valves are crucial. They must meet not only technical requirements for system operation but also considerations of safety, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. For instance, in petrochemical industries, control valves adjust fluid flow according to production needs, while safety valves serve as the final line of defense to ensure system safety during unforeseen emergencies.
In conclusion, control valves and safety valves are integral yet complementary components of pipeline systems. Their proper application and efficient operation not only ensure system stability and safety but also enhance production efficiency and equipment utilization. Therefore, a professional understanding and precise operation of these valves are indispensable in engineering design, equipment selection, and daily maintenance practices.

