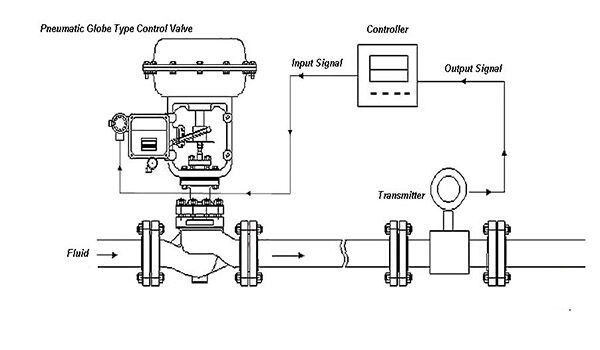
Understanding Pneumatic Control Valve Principles
In modern industrial control systems, pneumatic control valves have become one of the ideal choices for engineers to control fluids and gases due to their simple and reliable characteristics. The sophisticated and efficient operation principles of pneumatic control valve provide precise flow and pressure control for various industrial applications.
1. Operation Principle
Pneumatic control valves utilize compressed air as a power source, employing a cylinder as an actuator along with control signals and auxiliary devices to achieve precise adjustment of process parameters such as flow and pressure. The operation principle includes several key points:
- Power Source: Utilizing compressed air as power enables pneumatic control valves to respond and adjust rapidly.
- Actuator: Employing pneumatic actuators, which are divided into single-acting and double-acting types, to control valve actions.
- Drive Signal: Typically using a 4-20mA signal as the drive signal, combined with accessories such as electric valve positioners and converters to regulate valve operation.
- Adjustment Action: Adjusting valves linearly or with equal percentage flow characteristics based on changes in control signals to meet the requirements of different process parameters.
2. Classification
Pneumatic control valves can be classified into different types based on their action forms and operating modes:
Action Form Classification: Two types, normally open and normally closed, distinguished based on the valve's action when it loses its origin or fails.
Operating Mode Classification: Air-to-open and air-to-close, distinguished based on the valve's action direction when air pressure changes.
3. Applications
Pneumatic control valves have wide applications in various industrial control systems, where their safety and rapid response characteristics make them suitable for multiple scenarios:
- Gas Pipeline Control: Used to regulate gas supply in combustion systems, adjusting fuel supply based on parameters like temperature; selecting air-to-open valves can enhance safety.
- Heat Exchange Equipment: Utilized to control the flow of cooling water, adjusting the supply based on material temperature; selecting air-to-close valves ensures safety.
In conclusion, pneumatic control valves play a pivotal role in industrial production. Through a thorough understanding of their operation principles, classification, and applications, we can better utilize this critical equipment to enhance production efficiency and ensure safety. In the future of industrial development, pneumatic control valves will continue to play an irreplaceable role, becoming an integral part of various process control systems.