Comparing Pneumatic Sleeve and Single Seat Control Valves
With the widespread adoption and development of industrial automation, pneumatic control valves have become increasingly prevalent in fluid control systems. Among the various types of control valves, pneumatic sleeve control valves and pneumatic single seat control valves are two common and widely used types. Although they share similarities in their working principles, there are significant differences in their structures and application scenarios. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison of these two types of control valves, delving into their advantages, disadvantages, and suitability.
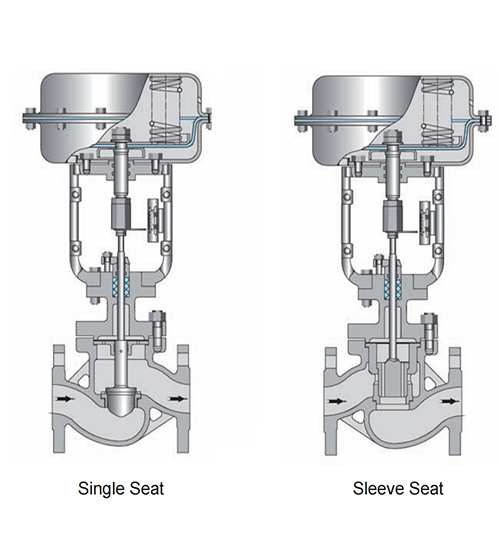
Structural Differences
Pneumatic sleeve control valves and pneumatic single seat control valves exhibit distinct differences in their structures, primarily in the design of their valve cores.
1. Pneumatic Sleeve Control Valve: The valve core of this type of valve adopts a sleeve structure, positioned inside the sleeve. When pneumatic pressure is supplied, it acts on the piston inside the sleeve, adjusting the fluid flow by controlling the piston's displacement. This simple structure is suitable for scenarios with relatively low demands on the medium. However, its range of adjustment may be limited due to the confinement of the sleeve.
2. Pneumatic Single Seat Control Valve: In contrast, the valve core of this type is independent, typically conical or cylindrical in shape, and directly contacts the valve seat. Pneumatic pressure acts on the valve core, altering its position to regulate the flow. The direct contact between the valve core and seat enhances stability and sealing, making it suitable for applications with high flow requirements and stringent medium control demands.
Differences in Control Modes
Pneumatic sleeve control valves and pneumatic single seat control valves also differ in their control modes, particularly in their application scenarios and usage.
1. Pneumatic Sleeve Control Valve: These valves are commonly used in on-off control systems, suitable for scenarios requiring frequent opening and closing. Due to their simple structure and easy maintenance, they find widespread use in applications where precise flow control is not critical.
2. Pneumatic Single Seat Control Valve: Ideal for continuous flow regulation, these valves enable precise flow control. They are widely applied in industries such as chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing, where strict control over flow rates and medium properties is essential.
Selection for Application Scenarios
When selecting the appropriate control valve, specific application scenarios and requirements must be considered.
1. For scenarios with relatively low medium demands and frequent flow changes, pneumatic sleeve control valves offer a practical and economical choice. They are commonly employed in various industrial applications, including water supply systems and HVAC systems.
2. For applications requiring precise flow control and stringent medium control, pneumatic single seat control valves are preferred. They are extensively used in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, where accurate control over flow rates and medium properties is crucial.
Pneumatic sleeve control valves and pneumatic single seat control valves each possess unique advantages and are suited to different application scenarios. When selecting control valves, it is essential to consider factors such as structure, control mode, and requirements for fluid control to ensure the stable operation and efficiency of the system. Choosing the appropriate control valve is a critical aspect of maintaining the stability of fluid control systems.
