Pneumatic Double-Seat Control Valves: Features & Installation
On this page
In the realm of industrial automation, the pneumatic double-seat control valve plays a crucial role as a fluid control device. Its unique working principle, multifunctional features, and various factors to consider during installation make it an ideal choice for engineers. This article delves into the working principle, features, and installation considerations of pneumatic double-seat control valves, providing a comprehensive understanding of its operational mechanism and key application points.
The working principle of a pneumatic double-seat control valve is based on the transformation of the medium fluid from the valve inlet through the throttling of the valve core and seat to the pressure behind the valve. This pressure then enters the upper chamber through the pipeline, exerting a force on the tray's top, which balances with the spring's counterforce, thereby controlling the pressure behind the valve. As the pressure behind the valve changes, the position of the valve core adjusts accordingly, thereby achieving flow rate regulation.
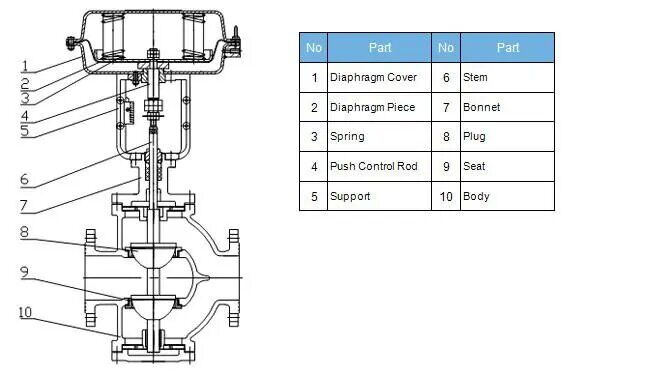
Pneumatic double-seat control valves consist of three main components: pneumatic actuator, valve body, and accessories. They operate using clean compressed air as power, receiving electrical signals or pneumatic signals to achieve precise flow regulation. The main features include:
1. Regulation Function
- Adjustment Speed: The speed of valve action is crucial for system operation. Pneumatic double-seat control valves can meet the system's requirements for valve speed, ensuring timely adjustments.
- Flow Characteristics: The relationship between valve opening and flow rate is the core of control valve operation. Different systems require different flow characteristic features, whether it be fast response or stable regulation.
- Low Opening Performance: Quality pneumatic double-seat control valves should have fine-tuning capabilities to ensure stable operation at low flow rates.
- Adjustable Range: The controllable flow range of the control valve determines its applicability. A wide adjustment range implies more flexible application scenarios.
- Flow Coefficient: The flow coefficient reflects the valve's ability to pass flow. For different types of valves, the size of the flow coefficient directly affects its regulation effect.
2. Shut-off Function
The shut-off function is another important characteristic of control valves. Valves with leakage of less than 0.001% can be considered to have excellent shut-off performance, ensuring the safety and stability of medium flow.
During the installation of pneumatic double-seat control valves, several factors need to be comprehensively considered:
1. Safety: It is imperative to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment during the installation process, avoiding accidents.
2. Location Selection: The installation location should have sufficient space for easy operation and maintenance, ensuring the convenience of disassembly and repair of the control valve and accessories.
3. Control Performance: The pressure loss of the piping system should align with the pressure loss considered when sizing the control valve to ensure the desired flow characteristics. Additionally, the inlet and outlet pipelines should maintain adequate straight pipe sections to ensure stable fluid flow.
4. Valve Group Matching: In the piping of the process, bypass valves are often installed alongside control valves to meet the continuous operation needs of equipment. During maintenance of the control valve, shut-off valves are used for isolation, and bypass valves are used for regulation.
Through the analysis provided above, we gain a deeper understanding of the features of pneumatic double-seat control valves and the factors to consider during installation. Comprehensive consideration of these factors will help ensure the stable operation and excellent performance of control valves.