What are Operational Considerations of Angle Control Valve
On this page
In automated control systems, control valves play a crucial role as one of the terminal control elements. They regulate the flow of media by changing the position of the valve core, thereby achieving adjustment and control of system parameters. Among these valves, angle control valves, with their unique structure and characteristics, serve as a notable variant. Below, we delve into their principles and operational considerations.
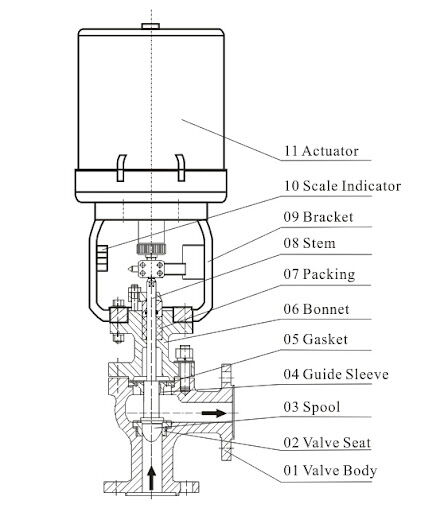
Angle control valves consist of two main parts: the actuator and the valve body. The actuator controls the movement of the valve core, while the valve body serves as the channel for media flow. In comparison with other types of control valves, angle control valves feature a angular design in the valve body, while the rest of the structure resembles single-seat valves. This design simplifies the flow path of angle control valves, reducing resistance, making them particularly suitable for regulating media with high pressure differentials, high viscosity, and containing suspended or granular substances.
In angle control valves, the position of the valve core determines the flow of the media. By altering the stroke of the actuator, the position of the valve core can be adjusted, thereby changing the cross-sectional area of the passage through the valve body and subsequently regulating the flow of the media. This capability enables angle control valves to achieve precise flow control, suitable for various industrial production scenarios.
As a critical component in automated control systems, angle control valves play a vital role in industrial production. However, several aspects need special attention during usage:
1. Comparison between Forward and Reverse Installation
Generally, angle control valves are installed in the forward direction, with bottom inlet and side outlet. However, in specific conditions such as high pressure differentials, high viscosity, susceptibility to coking, and media containing suspended particles, reverse installation, i.e., bottom inlet and side outlet for materials, is recommended. Reverse installation helps to improve imbalance forces, reduce valve core wear, and facilitate the flow of specific media, preventing clogging and coking.
2. Analysis of Reverse Usage
When using angle control valves in reverse, it's essential to note that changing the flow direction affects the resistance values, thus influencing the flow capacity of the control valve. Especially during trial production stages where process conditions are unstable, the control valve may remain at a small opening for extended periods, leading to oscillations and valve core damage. Therefore, during reverse usage, efforts should be made to avoid prolonged periods of small openings, particularly during trial runs.
3. Ensuring Safe and Stable Operation
Overall, angle control valves are suitable for forward usage in most situations, with reverse usage recommended only under specific conditions. Regardless, ensuring the safe and stable operation of control valves is paramount. Correct installation and usage methods can maximize the performance of angle control valves, ensuring the stable operation of systems.
By adhering to the aforementioned considerations, the efficiency of angle control valves can be effectively enhanced, ensuring the normal and safe operation of industrial production.
As one of the core components of automated control systems, angle control valves play an irreplaceable role in industrial production. Understanding their principles and operational considerations can better safeguard the safety, stability, and efficiency of industrial production.