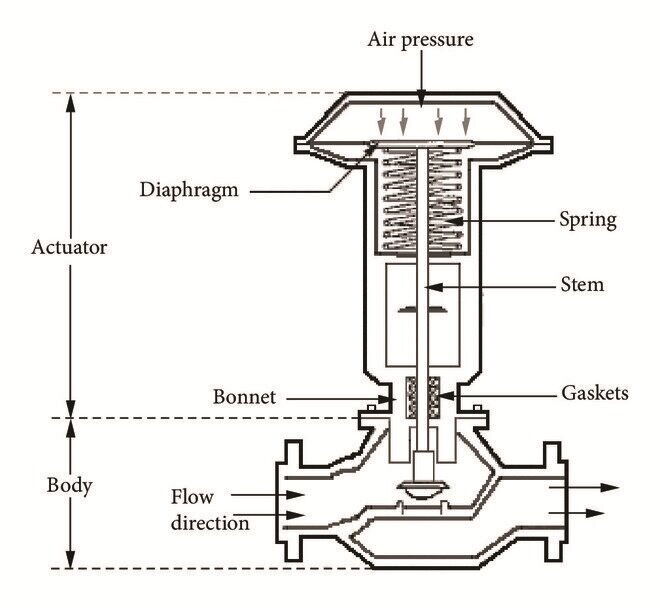
What are Key Performance Indicators of Control Valves
Control valves play a crucial role in industrial automation, and their performance indicators directly affect the stability and efficiency of systems. In addition to common indicators such as strength, sealing, and appearance, control valves also have some special performance indicators that require special attention, including flow coefficient, flow characteristic, rangeability, and control accuracy. Below, we will introduce these performance indicators and their impacts in detail.
1. Flow Coefficient
The flow coefficient is an important indicator for measuring the flow capacity of control valves, which includes the rated flow coefficient (Kv) and the relative flow coefficient (P). Kv represents the flow rate of water passing through the control valve under certain conditions when the pressure difference across the valve is 0.1 MPa. On the other hand, the relative flow coefficient P is the ratio of the flow coefficient under relative stroke to the rated flow coefficient, which can be used to calculate the relative valve opening. The calculation and comparison of these coefficients are crucial for selecting the appropriate size and type of control valves.
2. Flow Characteristic
The flow characteristic of control valves describes the relationship between relative flow and relative displacement when the medium passes through the valve. In actual working conditions, the flow rate of the valve may vary with pressure drop due to various factors. To facilitate analysis, the pressure drop across the valve is often set to be constant, resulting in inherent flow characteristics and working flow characteristics. Common inherent flow characteristics include linear, equal percentage, parabolic, and quick-opening characteristics, among which linear and equal percentage are more common. Linear flow characteristic is sensitive at small openings but difficult to control, while equal percentage flow characteristic allows flexible flow adjustment based on stroke changes, which is beneficial for the stable operation of systems.
3. Rangeability
Rangeability of control valves refers to the ratio of the maximum flow rate to the minimum flow rate that they can control, also known as the adjustable range. In practical applications, the minimum flow rate and leakage rate are different. The minimum flow rate refers to the lower limit value of the adjustable flow rate, while the leakage rate is the amount leaked when the valve is fully closed. Understanding and controlling the rangeability properly can ensure the stability and flexibility of systems under different operating conditions.
4. Control Accuracy
The control accuracy of control valves includes basic error, hysteresis, and dead zone. The basic error refers to the maximum deviation between the actual characteristic curve and the specified curve, while hysteresis represents the maximum difference between the corresponding stroke values when the same input signal rises and falls. The dead zone refers to the range where changes in the input signal do not cause any noticeable changes in valve flow. The accuracy of these indicators directly affects the performance and stability of control systems, requiring precise control and adjustment during design and operation.
In conclusion, the performance indicators of control valves have a significant impact on the stability and efficiency of systems. It is essential to fully consider these indicators in selection, design, and operation to ensure the normal operation and performance optimization of systems.