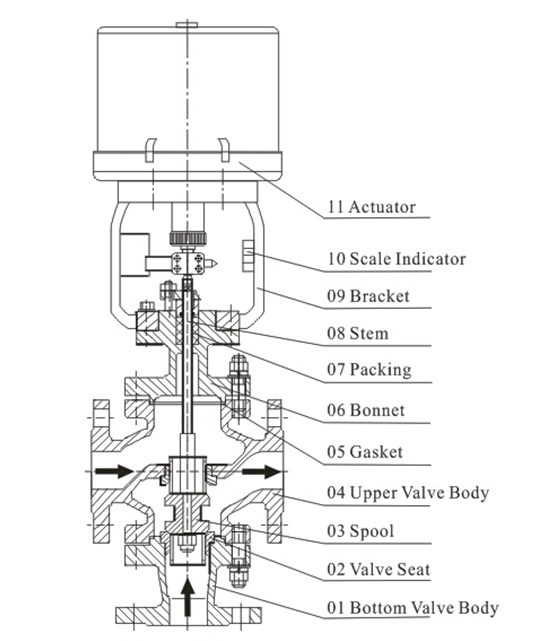
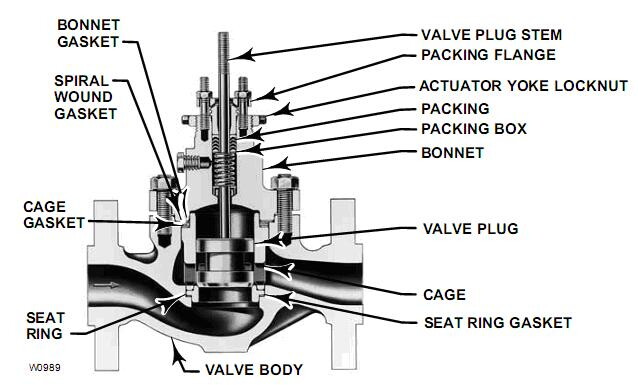
Comparing Pneumatic and Electric Control Valves
On this page
Control valves are essential in industrial production for regulating fluid flow, temperature, and pressure in pipelines, ensuring smooth operations. Pneumatic and electric control valves are two commonly used variants, each with advantages and disadvantages. A thorough consideration of factors is required when selecting the control valve with suitable actuator to meet production demands and enhance efficiency. This article outlines the characteristics of control valves with pneumatic and electric actuators to aid in understanding their applications and pros and cons in industrial production.
Pneumatic control valves represent a common type of control valve, operating on the principle of utilizing compressed air as a power source to regulate the valve's opening and closing through a cylinder actuator. These valves feature a straightforward structure that is easy to comprehend and operate. Equipped with accessories such as electric/pneumatic valve positioners, converters, solenoid valves, and position-lock valves, pneumatic control valves can achieve precise valve control. Their advantages include:
- Simple Structure: Easy to maintain and operate, boasting high reliability.
- Stable Operation: Demonstrates stable and dependable characteristics during operation.
- High Output Force: Compressed air as the power source enables the provision of substantial output force.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Comparatively budget-friendly when contrasted with other valve types.
- Fire and Explosion Resistance: Suitable for application in environments prone to flammability and explosiveness.
However, pneumatic control valves also present some drawbacks:
- Longer Response Time: Typically exhibit longer response times, limiting their application in certain high-demand processes.
- Limited Signal Transmission Distance: Unsuitable for remote control and signal transmission.
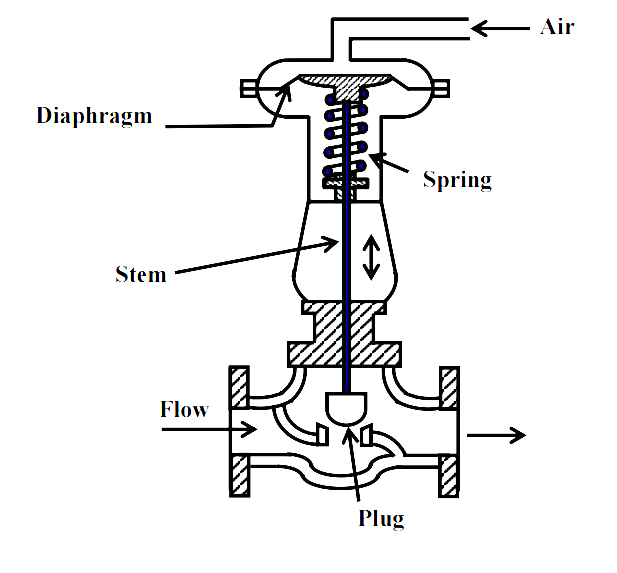
- Remote Control: Capable of remote and intelligent control, suitable for scenarios requiring long-distance control.
- Fast Response Speed: Exhibits a faster response speed, enabling quicker adjustment of pipeline media.
- Energy Efficiency and Environmental Friendliness: Consumes electricity only during operation, with zero carbon emissions.
- Convenient Installation: No need for complex pneumatic pipelines and air pump stations, making installation simpler.
Nevertheless, electric control valves also possess certain drawbacks:
- Complex Structure: Relatively more intricate structure compared to pneumatic control valves, leading to higher maintenance and repair costs.
- Lower Thrust: Typically provide lower thrust output compared to pneumatic control valves.
- Higher Cost: Generally priced higher than pneumatic control valves.
- Weaker Explosion-Proof Performance: Less suitable for environments with high explosion-proof requirements.